This article is a contribution from the accounting firm Milestone. If you would like to share quality content for startups in the form of a contribution, please contact the Venture Square editorial team at editor@venturesquare.net.

How to handle consignment sales exports under the Value Added Tax Act
As Korean products gain popularity overseas, the number of companies achieving growth in overseas markets is increasing. In line with this trend, many are establishing overseas subsidiaries to facilitate product sales in overseas markets. In some cases, these overseas subsidiaries are used for consignment sales and export transactions, which require tax treatment for the zero rate under the Value Added Tax Act. Therefore, this column will explore how to handle consignment sales and export transactions under the Value Added Tax Act.
Small business transactions
According to the Value Added Tax Act, if the supply of goods constitutes an export, the zero rate applies to the supply. Exports subject to the zero rate include transactions involving intermediary trade, as defined by Presidential Decree, and transactions where a contract and payment are made at a domestic business location. Consignment exports are exports of goods without exchange, under a contract where payment is made only to the extent of the goods sold. These exports are included in the zero rate transactions defined by Presidential Decree.
Timing of supply of goods
Meanwhile, the time of supply for consignment sales exports is when the supply price of the exported goods is determined. Therefore, reporting must be based on the actual amount sold to consumers locally.
Value-added tax base
When export proceeds are received in foreign currency, the VAT base is the amount converted into Korean Won before the time of supply. If the proceeds are received after the time of supply, the VAT base is the amount converted using the base exchange rate or arbitrage rate under the Foreign Exchange Transactions Act at the time of supply. In this case, accounting revenue must be recorded at the time the product is sold to the local consumer, and the overseas subsidiary must remit the amount minus the service fee.
Meanwhile, there may be cases where the export amount reported in the export declaration differs from the actual sales amount. In this case, the estimated loading amount should be provisionally reported when filing the export declaration. Once the amount is confirmed through overseas sales or payment is received, the actual supplied amount can be reported within 60 days of that date using an export declaration correction application.
Attached documents for small business tax rate
The following are the attached documents to be submitted when filing a value-added tax return .
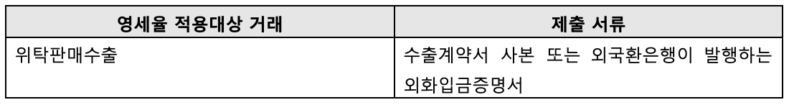
In this case, if the payment is inevitably delayed after the sale and only a portion of the foreign currency deposit certificate is issued , according to the relevant regulations, a foreign currency acquisition statement must be submitted for the unpaid portion, and when the foreign currency is deposited thereafter, the foreign currency deposit certificate must be marked as a previously reported portion and submitted when reporting .
- See more related columns
You must be logged in to post a comment.