The Ministry of SMEs and Startups (Minister Oh Young-joo, hereinafter referred to as the Ministry of SMEs and Startups) and the Smart Manufacturing Innovation Promotion Team (Director Ahn Gwang-hyun, hereinafter referred to as the Promotion Team) announced the results of the ‘1st Smart Manufacturing Innovation Survey’ on the 28th.
This survey is the first to be conducted since the enforcement of the 'Act on Promotion of Smart Manufacturing Innovation by Small and Medium Enterprises' (July 2023). After conducting preliminary survey planning such as population composition and questionnaire design through a research group comprised of experts in each field, a sample survey was conducted.
In order to clearly define the target of the smart manufacturing innovation policy, including the spread of smart factories, 163,273 small and medium-sized manufacturing companies with factories among the 633,182 companies engaged in manufacturing as of 2023 were set as the population, and a face-to-face survey was conducted from October 2024 to January 2025 using 5,000 of them as a sample.
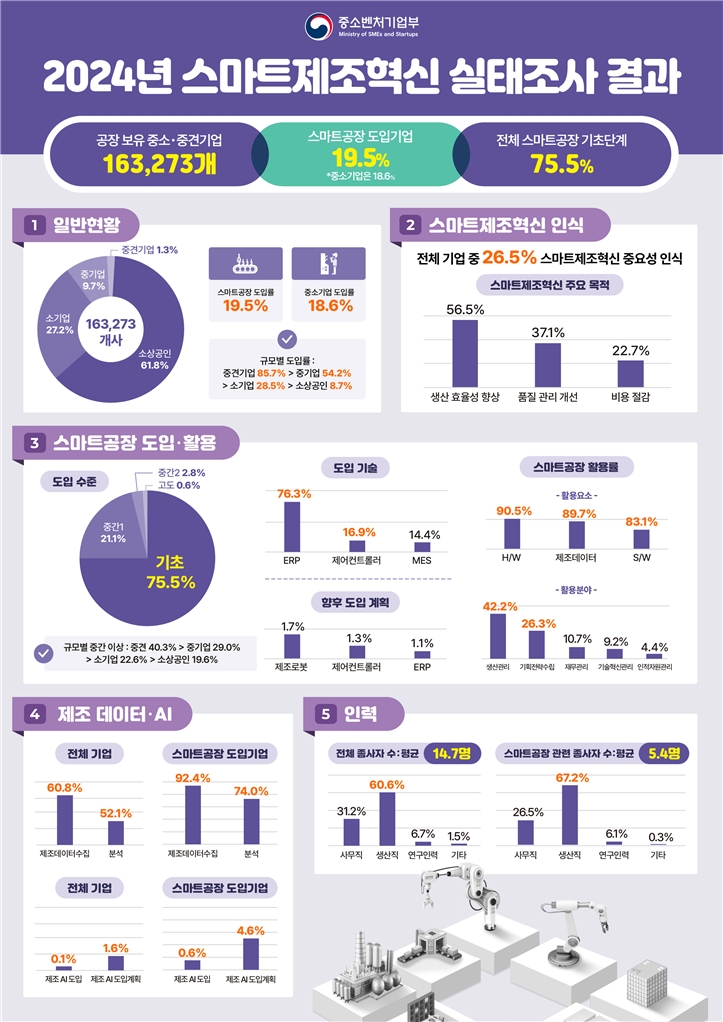
◆ (General Status) Among small and medium-sized companies with factories, 19.5% have introduced smart factories.
According to this survey, among the 163,273 small and medium-sized manufacturing companies with factories, small business owners account for 61.8%, small businesses account for 27.2%, medium-sized businesses account for 9.7%, and medium-sized businesses account for 1.3%.
The smart factory adoption rate was 19.5% for all companies and 18.6% for small and medium-sized companies, and it was confirmed that the adoption rate increases as the company size increases.
◆ (Awareness of Smart Manufacturing Innovation) 22.8% of all companies recognize its importance and implement it
Awareness of smart manufacturing innovation was found to be that approximately 22.8% of all companies recognize the importance of smart manufacturing innovation and are actually introducing or utilizing it, and 26.5% of all companies stated that smart manufacturing innovation is important.
The main purpose of promoting smart manufacturing innovation is to improve production efficiency (56.5%), followed by improving quality management (37.1%) and reducing costs (22.7%).
◆ (Introduction and utilization of smart factories) Basic level smart factories are 75.5%, utilization rate is 80% or higher
Among the companies that have introduced smart factories, 75.5% are at the basic level, and it was confirmed that the level of smart factories increases as the size of the company increases. The scope of smart factory introduction was found to be 99.8% of partial introduction.
The average cost of introducing a smart factory was found to be 1.13 billion won for small and medium-sized enterprises, 750 million won for small and medium-sized enterprises, and 46.4% of the respondents introduced solutions through external specialized companies, while 45.9% used their own specialized personnel.
The most common method of funding at the time of introduction was self-funding (56.9%), and the average cost of self-construction was found to be 810 million won.
The main technologies being introduced are ERP (76.3%), control controller (16.9%), and MES (14.4%), and the technologies planned for introduction in the future are manufacturing robots (1.7%), control controller (1.3%), and ERP (1.1%).
The smart factory utilization rate exceeded 80% for all components, and when examined by component, H/W was 90.5%, manufacturing data 89.7%, and S/W 83.1%.
The field in which smart factories are mainly utilized is production management (42.2%), followed by business planning and strategy formulation (26.3%), financial management (10.7%), technological innovation management (9.2%), and human resource management (4.4%).
45.7% of companies said that they need to improve the level of utilization of smart factories, and 25.6% of companies have their own investment plans for improvement.
◆ (Manufacturing Data·AI) Manufacturing data collection companies account for 60.8% of the total, and manufacturing AI introduction companies account for 0.1%.
Companies that are collecting manufacturing data account for 60.8% of the total, and 52.1% of them are conducting actual analysis. 92.4% of companies that have introduced smart factories are collecting manufacturing data, and 74.0% of them are analyzing it.
It was confirmed that 0.1% of all companies have introduced manufacturing AI, and 1.6% of all companies have plans to introduce it. In the case of companies introducing smart factories, it was found that 5.2% have introduced manufacturing AI or have plans to do so.
The percentage of companies with dedicated departments and personnel related to manufacturing data and AI was 0.8%.
◆ (Human Resources) Out of 14.7 employees, 5.4 are related to smart factories
The average number of employees within a company is 14.7, of which 60.6% are in production, and 5.4 people, or 36.7% of all employees, are involved in smart factories.
19.5% of all companies have a dedicated department or staff for smart factories, and 6.6% of companies have set aside a separate budget for related training.
Among companies planning to increase additional manpower related to smart factories, 14.5% of the total were found to be companies, and the biggest reason for not increasing manpower was found to be cost burden (47.1%).
Regarding these results, Kwon Soon-jae, head of the Manufacturing Innovation Division, explained, “This is the first official survey examining the achievements and challenges of the smart factory policy being promoted for the digital transformation of small and medium-sized manufacturing sites,” and evaluated, “The digital transformation of small and medium-sized manufacturing sites is currently in progress, with a smart factory adoption rate of 19.5% (31,782 companies) and basic smart factories (75.5%).”
In addition, based on these results, the government stated that it plans to “continuously promote smart factory distribution policies to promote DX in small and medium-sized manufacturing sites, establish regional specialized manufacturing AI centers to spread manufacturing AI on the basis of manufacturing DX, and foster manufacturing AI specialized companies to create a manufacturing DX/AX ecosystem.”
- See more related articles
You must be logged in to post a comment.